STARBUCKS SUSTAINABILITY REPORT
This work focuses on integrating sustainability into Starbucks’ business strategy at global scale. Through research and systems analysis, we identified opportunities across operations, supply chain, and customer experience to drive efficiency, resilience, and brand trust. The result is a practical roadmap that treats sustainability as a core business advantage.
DETAILS:
Sustainable Business Strategy
TEAM:
Rose Toal, Ananya Srinivasan, Subin Cho



Project Brief:
The objective of this project was to design a user-focused innovation that encourages sustainable behavior among users while fostering real improvements in Starbucks’ sustainable practices. Our research approach combined both qualitative and quantitative methods to obtain a thorough understanding of Starbucks’ customer behaviors, perceptions, and needs. Through the synthesis of insights from diverse sources, our goal is to provide guidance for the creation of a user-focused innovation that is not only memorable and impactful but also drives tangible market-ready improvements.
Generative Research:
The brand’s iconic status and cultural influence were considered, along with the intricate details of its design system, from the recognizable green color to the symbolic Siren logo. Starbucks’ consumer strategy, sustainability commitments, and current challenges were scrutinized, emphasizing its engagement in social media, customer experience, and commitment to environmental sustainability.
We also conducted a material life cycle analysis specifically on Starbucks’ hot coffee cups, examining the environmental impact of single-use cups, recycling challenges, and the need for a sustainable alternative. Our research highlights Starbucks’ potential to reshape industry norms by prioritizing ethical practices, waste reduction, and sustainable innovation.
Beyond the charming interiors and the allure of a perfect latte, Starbucks holds the potential to reshape the way we view our world and the resources within it. By fostering a mindset that embraces responsible consumption, Starbucks’ influence has the potential to ripple through industries, inspiring others to follow suit.

Business Analysis:
Our research delves into the intricacies of the global coffee market, with a focus on Starbucks, which commands a substantial 39.3% market share in the $47.4 billion U.S. retail coffee market. The strategy canvas reveals Starbucks’ industry leadership in revenue, store count, and customer ratings. The stakeholder map emphasizes the collaborative nature of Starbucks, requiring cooperative efforts to achieve sustainability goals with partner companies.
Consumer segmentation identifies two groups: the busy coffee lover and the experience seeker. Gaps in Starbucks’ reputation highlight areas for improvement, necessitating active monitoring of changing consumer preferences. The AUDIO analysis underscores climate change threats and waste challenges, advocating for a zero-waste coffee cup and public commitments to sustainability goals.
While Starbucks is renowned for top-quality coffee, waste management, supply chain challenges, and distant sustainability goals pose significant challenges. Swift action is essential for minimizing environmental impact, meeting targets, and inspiring positive change within the industry. Our research provides a concise overview, urging Starbucks to align operational practices with sustainability goals in the evolving global landscape.
Primary Research:
The goal of our primary research was to facilitate positive behavior change, enhance environmental initiatives, and align services with customer preferences. We utilized an online survey that investigates factors driving brand loyalty, ordering habits, and customer satisfaction.
We conducted an online survey with a total of 366 responses. The survey was designed to gain a comprehensive understanding of the mindset, habits, and preferences of Starbucks customers with regards to sustainability and waste management, as well as their loyalty towards the brand.
We interviewed eight Starbucks customers utilizing audio recordings and automatic transcription. From these interviews, clear themes emerged: customer experience, convenience, efficiency, customization, and enjoyment of seasonal drinks. A positive digital experience and a comfortable atmosphere are also important factors. Customers’ loyalty, rewards program, and familiarity with Starbucks play a role in their choices. Additionally, sustainability and eco-friendly practices are becoming a priority for users, but they have concerns about Starbucks’ efforts in this area due to lack of transparency and communication.
In-person observations using the AEIOU framework reveal correlations between store layout, ambiance, and customer behavior, providing insights into how Starbucks outlets create unique atmospheres influencing consumer choices.

Data Analysis:
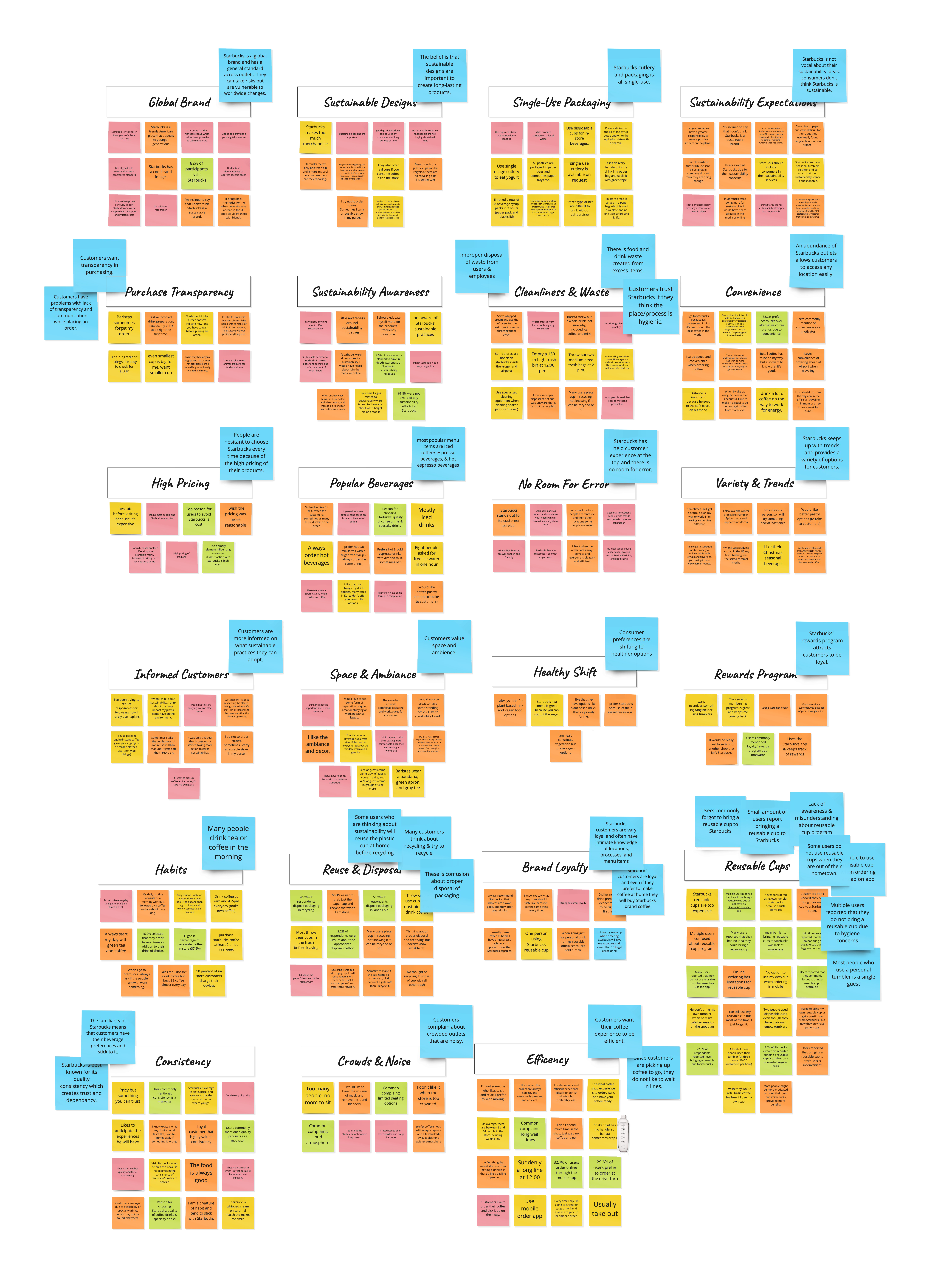
Using affinity mapping and cross-cluster analysis, we conducted a thorough exploration to reveal valuable insights. Our mission was to understand Starbucks’ current state and identify the path toward a sustainable and consumer-centric future. During this process, we engaged in the exploration of significant themes.
To improve sustainability and meet customer demands, Starbucks must address limited awareness and communication, as well as perception issues around prioritizing sustainability. Enhancing the rewards program and providing additional benefits could be a key driver towards more sustainable behaviors.
Overcoming barriers to sustainable behavior, such as hygiene concerns and confusion about disposal methods, is crucial for customer adoption. Starbucks also has the opportunity to proactively adapt its menu to cater to evolving consumer preferences, placing a strategic emphasis on sustainable choices. Waste management presents an opportunity for Starbucks to address improper disposal practices and reduce environmental impact from excessive food and drink waste.
Leveraging its global standardization approach, Starbucks can embrace risk-taking and innovation across various markets to reinforce its commitment to sustainability.
solution:
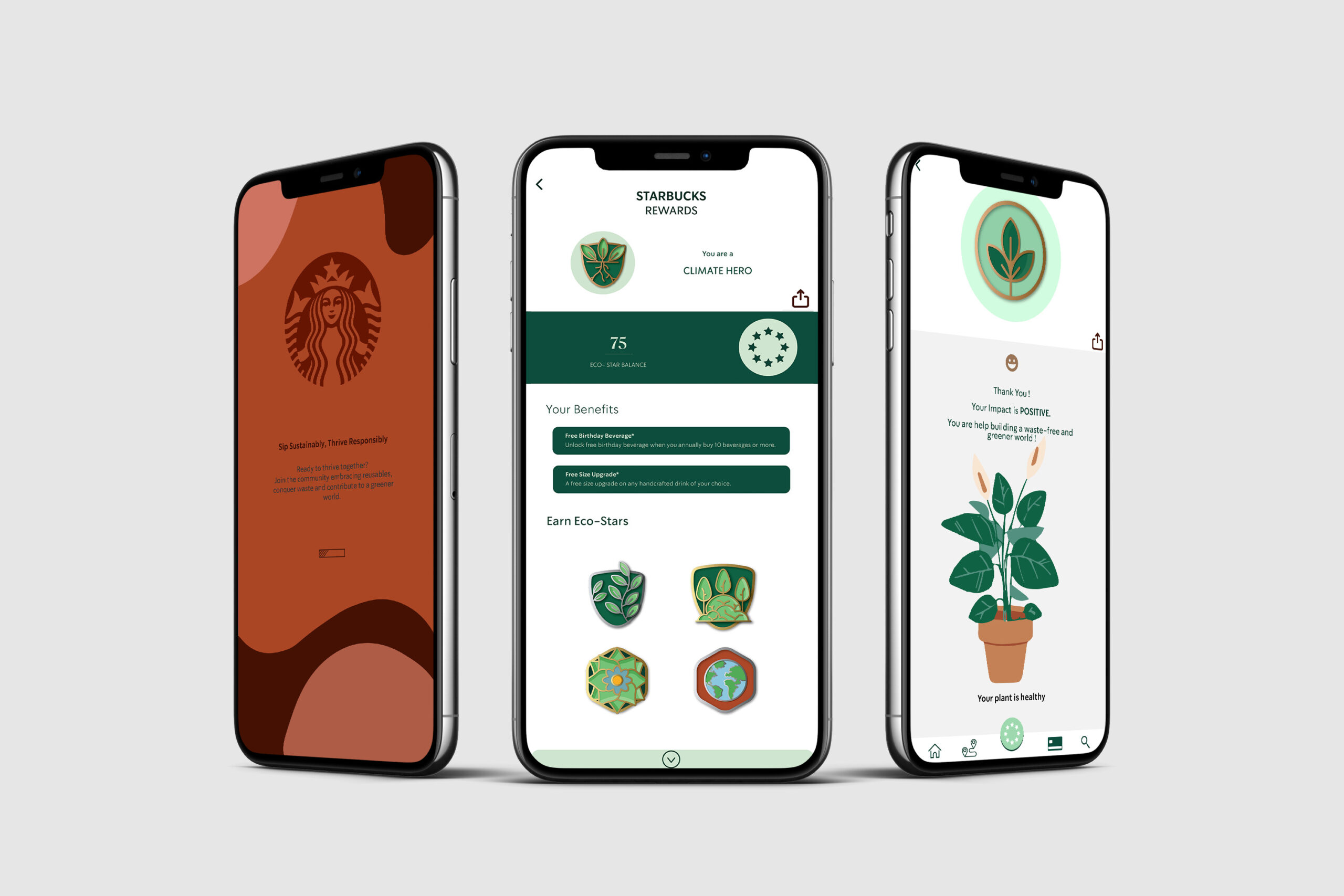
It’s evident that true sustainability cannot be achieved with single-use products. With the escalating impacts of climate change, time and options are dwindling. Our solution introduces three key innovations to drive lasting behavior change, combat Starbucks’ to-go culture, and address single-use product challenges. Starbucks reports that 8% of customers consistently opt for reusable cups over disposables. According to the diffusion of innovation model by Everett Rogers the milestone for successful innovation adoption stands at approximately 20%. With the implementation of these initiatives, we are confident that Starbucks can exceed this threshold, thereby actualizing long-term sustainable change and successfully attaining its sustainability goals – even surpassing them.
Solve The Cup Dilemma
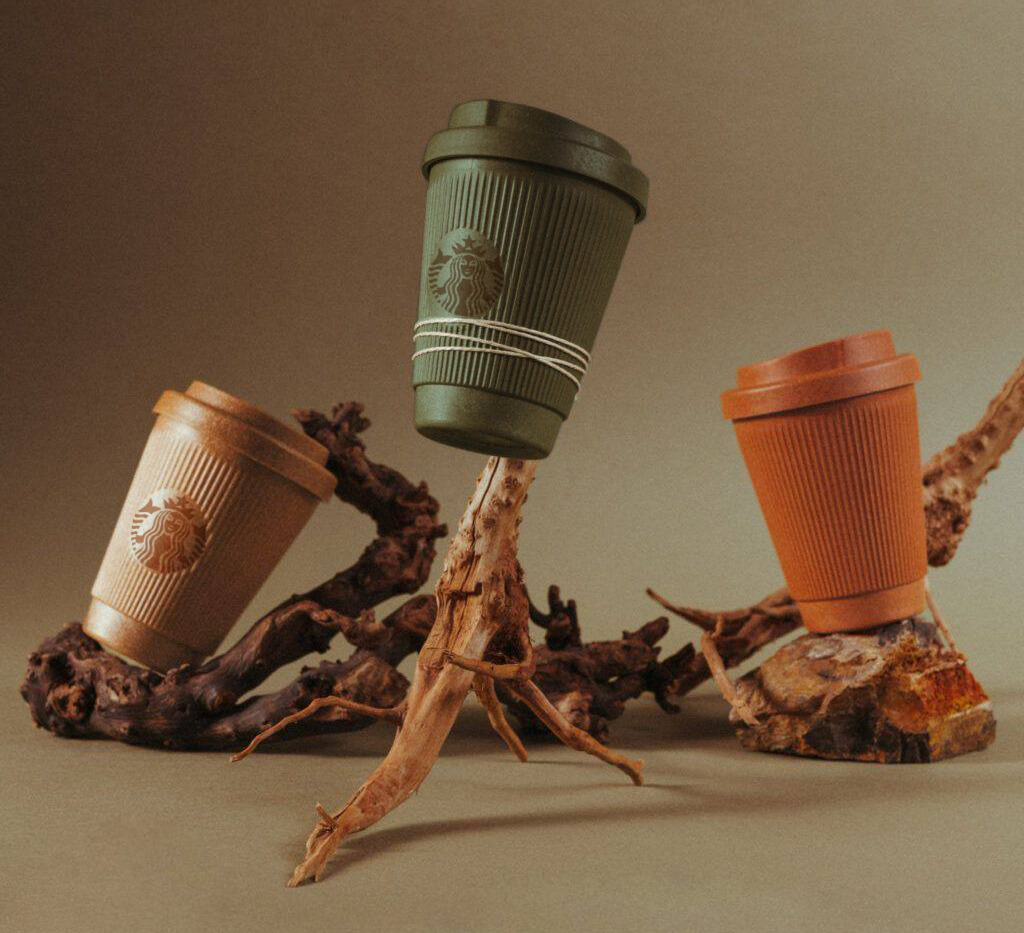
A primary goal for our solution is to transform Starbucks into a circular economy by eliminating single-use cups. To promote reusable cups, we must address Starbucks’ waste problem. As a first step, we will partner with German company Kaffeform to manufacture reusable coffee cups from coffee waste.
Create Behavior Change
Our new app design enhances the rewards program by creating tangible sustainability metrics, benefits, reminders, and gamification that reusable cup adoption. Our new app design employs prompts, feedback, and modeling for easy sustainable participation, aided by triggers and reminders.
Encourage Innovation Adoption
In-store, captivating visuals will help normalize sustainable behavior. Dedicated screens will show customer names, eco badges, wait times, and amplify social norms, addressing wait time concerns and making sustainable behavior desirable.